There are many best practices for SEO, including those provided by Google.
Here are 17 tips that can help you develop a better search presence.
What Do Best Practices For SEO Even Mean?
Contents
- 1 What Do Best Practices For SEO Even Mean?
- 2 1. Choose The Best Platform For Your Situation
- 3 2. WordPress SEO
- 4 3. Website Builder Platforms For Easy SEO
- 5 4. Fast Web Hosting
- 6 5. Title Element (AKA Title Tags)
- 7 6. Alt Text
- 8 7. URL Structure
- 9 8. Best Way To Use Headings For SEO
- 10 9. Google Discover
- 11 10. AI For Content
- 12 11. SEO For Images
- 13 12. SEO For Product Pages
- 14 13. Best Practices For Category Pages
- 15 14. Best Practices For Review Websites
- 16 15. Structured Data For SEO
- 17 16. Best Way To Do Internal Linking
- 18 17. Read Patents Carefully
- 19 Understanding SEO
- 20 How can I improve my search engine ranking?
- 21 How does Google rank its search results?
- 22 What is the elements of Google?
- 23 What are the main pillars of SEO?
SEO best practices are generally considered to be those that adhere to Google’s evolving guidelines and are not explicitly listed as manipulative by Google.
But best practices aren’t just about what Google considers manipulative and what isn’t.
For example, Google’s guidelines don’t tell you how to choose hosting, how to optimize a WordPress site, or whether a website builder makes the most sense for a particular situation.
These are the types of best practices that this guide will cover.
1. Choose The Best Platform For Your Situation
A good place to start is before any code is uploaded to the web.
Understanding the technology behind a web presence is important to making the best SEO choices.
Get this part right and the site will be well positioned to sprint to the top spot.
Why Choose Self-Hosted
Today’s choices are between a CMS (content management system) that resides on the publisher’s server and a site building platform where the technology is hosted and managed by the provider.
Many people choose self-hosted open source solutions (such as WordPress) because of the extensive support and development network, which provides complete freedom to build custom websites that users can optimize with no limits other than their own skill level.
The downside of self-hosted solutions is the need for technical skills to optimize templates, deal with constant updates, and acquire the necessary knowledge to create a strong security posture against hacking.
Why SaaS Platforms Make Sense
Many companies prefer to focus on business rather than maintaining website technology.
A lawyer’s skill is to litigate, not to learn how to switch to the system font stack on their self-hosted CMS.
For businesses that prefer a high-performance website without the need to deal with technology, a SaaS (software as a service) website building platform is increasingly considered the best choice for many small and medium-sized businesses.
Examples of Software as a Service (SaaS) platforms:
The best practice, then, is to audit what a company needs to do business online and then see which technology works best – a self-hosted CMS or a SaaS website building platform.
2. WordPress SEO

There are many CMSs to choose from.
WordPress is probably the most popular open-source, free system with a huge global community of developers supporting it, including SEO.
Anyone with a moderate understanding of how to use WordPress can build an entire website for next to nothing.
This includes free templates and free SEO plugins, plus all the other plugins to extend the functionality, such as the WooCommerce plugin for creating e-stores with a budget of $0.
Web development and SEO expert Adam J. Humphreys of digital agency Making 8 Inc. shared his thoughts on best practices for WordPress SEO.
“With WordPress, something as simple as a default theme will achieve website speed goals without a lot of work.
Add a good host with a Content Delivery Network (CDN), a compression plugin like WP Rocket & ShortPixel, and the result is a very fast website. We’re talking 0.5 second load times, and that’s not going to happen on some paid solutions.
My favorite SEO plugin is RankMath Pro because it allows me to generate a schema, generate local SEO page content, create video sitemaps, and do things that other plugins just don’t do.
A plugin like this allows me to highlight content for search engines in a way that I’ve never seen with any paid solution outside of WordPress.
A WordPress builder like Bricks Builder is a template system that allows you to create custom SEO optimized themes that load websites in a fraction of a second out of the box before even compression.
These days, I think dentists using WordPress have better websites than many Fortune 500 companies, and I know this because I’ve done technical SEO audits for them.
WordPress can be the best for SEO and security, assuming you have a simple maintenance plan and have someone to click update a few times a month (yes, it really is that simple).
The finished site using WordPress is basically set up. There is no longer a need to have a full-time developer to keep up with basic security updates.”
I asked Matt Cromwell, WordPress expert and co-founder of @GiveWP, to share some WordPress SEO best practices.
Matt offered the following insights:
“People who build websites with WordPress and want to focus on Web Core Vitals often start with caching plugins and whatnot. That is a mistake.
The two biggest drivers that will make your website faster are: (1) great hosting and (2) clean markup.
Throwing a lot of caching at your WordPress site may help some on really slow hosts, but it will never give you the performance you really want. So start from scratch with fast hosting.
The biggest factor affecting your markup is a combination of your theme and, most often, your page builder.
Most websites that work really well use a minimal theme that works well with WordPress’ built-in content editor (known as Gutenberg). Page builders are often the biggest factor in slowing down a website. Or you have to do a lot of custom code to reduce their impact.
So my biggest recommendation for small businesses who don’t want to overburden their site and keep it lean and functional is to invest in highly efficient hosting, keep their theme minimal, and use a WordPress editor instead of a page builder.
Once you grow your business enough to hire talent, hire a great web developer and digital marketing expert to make your site beautiful and fast.”
Andrew Wilder of WordPress support company NerdPress offered a WordPress SEO best practice idea, one related to fonts.
“We see a lot of sites using a lot of web fonts – they can really slow things down if they’re not implemented well.”
These are particularly challenging because they have to be loaded early in the process (so the page can be rendered properly), and when they are loaded, they can cause layout shifts as the text first displayed changes font.
Switching to a system font (which uses the default/system font regardless of the device the user is on) can make a huge difference in performance.”
3. Website Builder Platforms For Easy SEO
Understanding how to choose the best way to create an online presence is an SEO best practice.
One way to create an online presence is through a SaaS website builder.
Not too long ago, SaaS website building platforms were great for building attractive websites, but not so good at website speed and SEO.
But that is no longer the case.
Today, major website builders match or surpass traditional CMS in terms of website speed and SEO.
Over 14 million websites have been built using Duda’s technology, and Wix has over 200 million users worldwide.
Focusing on SEO, the main advantage of website building platforms is that they take care of technology, integrate directly with Google business profile, produce valid structured data, output on-page SEO that complies with Google guidelines and excels in speed and website performance. .
A platform like Wix makes it easy for businesses to get online and start competing with great SEO.
A platform like Duda is easy to use for business owners. However, it is designed to meet the needs of digital agencies and service providers who can use Duda’s platform to quickly roll out attractive websites with fast performance that are flexible for customization and SEO.
Duda’s platform handles the underlying technology, for example, optimizing the page for speed, integration with a CDN (content delivery network), and semantic markup such as section elements.
This allows agencies and developers to focus on what’s important: content, promotion and SEO.
Anton Shulke, Duda’s Head of Influencer Marketing, explained:
“The seo settings that Duda offers website builders are very user-friendly and really help their website stand out from the rest.
In addition to providing users with website SEO settings in our builder, we provide users with educational materials not only about our platform but also about what SEO is and why it is important.
Duda has created technology that optimizes our customers’ websites for SEO in the background, so our clients can focus on designing their sites.
Duda takes care of complex optimization such as code optimization for Core Web Vitals, generating robots.txt files, sitemaps and even submitting web pages to be indexed immediately upon publication.
Duda’s platform not only focuses on providing excellent out-of-the-box site optimization, it also gives clients the opportunity to optimize their business listings with options such as the Local Business Scheme and app integrations with Uberall and Localeze, making Duda a great choice for both web designers and business owners.”
4. Fast Web Hosting
Using a fast web hosting environment is the best SEO best practice – as is choosing the most suitable web hosting platform.
Examples of different types of web hosting:
The best SEO practice for hosting is to choose the fastest possible web hosting that also makes economic sense.
Optimizing website speed depends on at least four factors:
Of those four, the first two (hosting and fast website) are under company control.
And of the two, fast hosting is arguably the most important — because a slow web host can make even a fast website run slow.
Shared hosting is the easiest way to set up a website (or multiple websites).
The downside of shared hosting is that the cheapest plans put thousands of sites on a single server, so all sites must share the limited resources of that single server.
This can result in slower websites, especially if any of the other websites on the server are under load.
Websites that are popular and use “too many resources” may experience slow traffic (called “throttling”).
Some might say it’s a good way to start and then expand as the site becomes more popular.
Once a website becomes popular, traffic will be reduced, which can slow down the website’s popularity – as slow websites drive away site visitors who would otherwise become customers or frequent visitors.
Many SEO professionals can agree that a shared hosting environment is fine for a hobby site, but not for a site with monetary goals.
Some premium shared hosting environments are not necessarily cheap, but are generally cheaper than renting an entire server.
The value of premium shared hosting is that it is easy to set up websites and access more server RAM and CPU resources.
Prices can range from $40 to over $100 per month.
Managed WordPress Hosting
Managed WordPress hosting is a specialized server environment specifically tailored for WordPress websites.
These hosting environments only run WordPress sites and offer features that offload tasks from the website, allowing WordPress sites to perform at a higher level.
The advantages of managed WordPress hosting are faster performance, better security and less effort in managing the technology side of WordPress.
David Vogelpohl, VP of Growth at WPEngine shared:
“Unlike generalist hosts, who also have to try to optimize their platform & caching for any type of site, managed WordPress hosts focus on one type of site, WordPress.
By focusing on one type of site, managed WordPress hosts can optimize their networks, caching and infrastructure to a much greater extent than is possible in general hosting environments.
The result of this focus is often a much faster site for you when hosted on a managed hosting provider.
Managed hosting providers like WP Engine will often deliver faster speeds for your site by offering secure and advanced caching for your site, a global content distribution network (CDN), low site-to-server ratio on shared hosting, and highly optimized infrastructure which is specific to the type of web pages they host.
In the case of WP Engine, we offer free & global CDN via Cloudflare for all customers and includes a proprietary caching layer called EverCache, which includes WordPress and WooCommerce specific optimizations that help make websites faster than off-the-shelf caching solutions built for any type of website.”
Website security is an SEO issue because website rankings start to drop after a website is hacked.
I asked David about WordPress security on a managed WordPress hosting service.
“Managed hosting providers like WP Engine can be a powerful part of your security toolkit, offering malware and virus threat management support helping you prevent malware before it becomes a problem, detect & remove malware when present and recover from malware infections that have affected your site.
Managed hosting providers often help prevent malware threats by offering Web Application Firewalls (WAFs), enforcing strong passwords, enterprise-grade SSO support, and forcing security updates for key software used on your website (WordPress, PHP, MySQL, etc.).
For example, 37% of WordPress sites are on PHP 7.3 or lower, which are not supported by security updates, while 100% of WP Engine users are on patched versions of WordPress and PHP.
Providers will also include network and server-level threat detection and blocking capabilities that can help prevent some attacks before they start, stop active attacks, or alert you to malware present on your site.
It’s also useful to increase your host’s security benefits by using a solution like WordFence or Sucuri to fully scan your site’s code for malware on a regular basis.
If your site has already been compromised by malware, managed hosts may offer remediation support (vulnerability repair/malware removal) depending on the nature of the malware and the vulnerability that may have led to the presence of the malware.
Once the malware is removed from your site, you can use daily backups, often provided for free by managed platforms like WP Engine, to recover your site.
Along with a sound security culture and practices within your own organization, choosing a managed host is an excellent foundation for keeping your website safe and secure.”
Virtual Private Server (VPS)
VPS is the next step forward that offers fast performance, but at significantly higher prices than shared servers.
The value of a VPS is greater control over the server environment.
The downside is that many VPS hosting environments require more technical ability to manage successfully. However, some VPS offers have a management option where the host provider will manage the server at an additional cost.
Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting is a specialized form of hosting.
In general, a cloud hosting environment is one where hosted data and processes are spread across multiple servers and have redundancy, so data loss is almost impossible.
The advantage of cloud hosting is that it is scalable and priced according to the resources used.
A site that experiences a sudden spike in traffic can be quickly scaled up through a cloud hosting environment at a higher cost.
One of the downsides of cloud hosting is that it can require more technical skills to manage.
Dedicated Server
Managing a dedicated server is not as difficult as it used to be, but there is still a learning curve.
Even with a relatively simple control panel like Plesk Onyx, while intuitive to use, it helps to know about PHP settings, firewall settings, NGINX, and Apache.
In general, there are no guardrails to protect you from mistakes on a shared server, so you have to know your way around.
The title tag is widely considered an important ranking factor.
What’s in the title element is important because it’s (usually) shown as the title link in search results.
As a result of this knowledge, SEO professionals often use the title tag as the place to write the target keyword. It’s a 20+ year SEO tradition.
But times have changed and Google rewrites the title link if it is not descriptive or contains repeating patterns.
This means that the best practice for title tags has changed.
Today, it is best practice for the title element to be descriptive, concise, and not common.
Adding a keyword is still useful there, but it’s important to be descriptive.
This means that when someone reads the title tag, they should know what the website is about.
If the title tag doesn’t pass that test, it’s probably not good enough.
The best practice today is to target the user intent of a keyword in the content and then target that user intent in the title tag.
For example, since 2000, the standard practice has been that if you are trying to rank for the keyword “fishing flies”, you must use the term “fishing flies” in the title tag.
This is no longer the case because that keyword phrase is vague, so Google will first identify the user’s intent behind that keyword and then rank sites that match the user’s intent – not the keyword in the title tag.
The best way to write a title tag is to understand the user intent of the keyword and try to match the intent in the title tag.
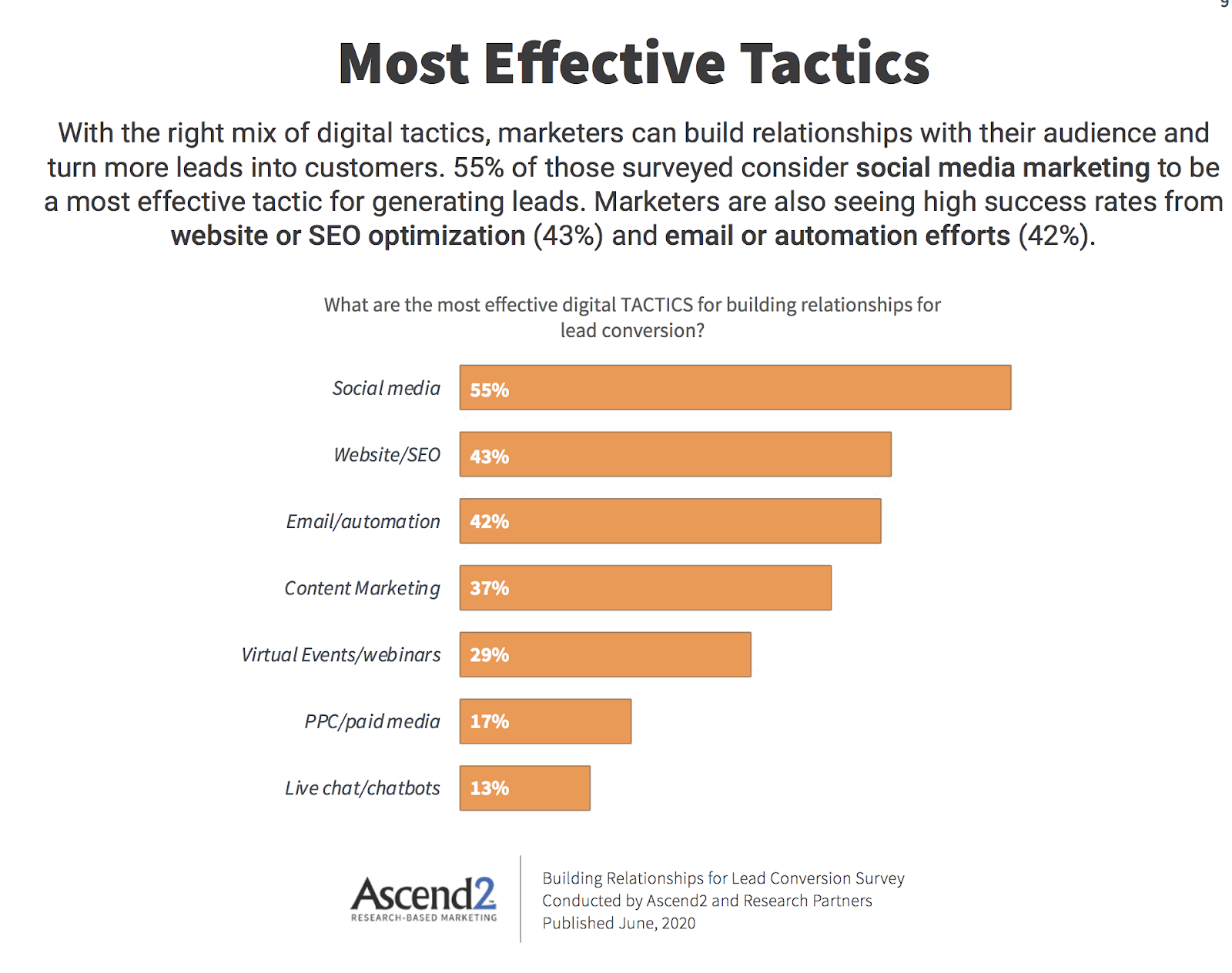
These are the search results for the keyword “fishing flies”:
Screenshot from a search for [fishing flies], Google, July 2022
What’s notable about the titles in the search results above is that none of the top four search results have the keyword “fishing flies” by itself.
A phrase or partial phrase is always in the context of a phrase that signals the user’s intent.
The number one search result isn’t even an exact match for the key phrase.
What those search results – and almost any search result – will show is that it’s not just the keyword in the title that matters, it’s important to say what the topic of the web page is in a way that also signals intent to the user.
That’s a best practice for title tags, in my opinion: Optimize your title tag for the user’s intent topic and don’t just throw out an exact match keyword phrase in the title element.
6. Alt Text
Alt text (aka alt tag or image alt attribute) is an HTML attribute of the HTML image element.
The purpose of alt text is to describe what the image is about.
The best SEO practice for using alt text is to describe what the image is about.
Casey Markee, founder of MediaWyse, offers a helpful way of thinking about alt text:
“Ask yourself, if someone with visual impairments was sitting next to you, how would you describe the photo on your computer screen to them?
Alt Text exists to describe a photo to someone who cannot see it.
It doesn’t exist to be stuffed with keywords, marketing jargon or other nonsense.
Finally, be sure to add a ‘period’ at the end of your alt text. It’s an indicator to screen readers that the alt text is complete.”
7. URL Structure
Many in the search industry mistakenly believe that Google uses words in the URL structure to understand what a page is about.
But that is not necessarily the case today.
Google has a long history of minimizing the importance of using keywords in a URL. Back in 2017, Google’s John Mueller said that keywords in URLs are overrated as a ranking factor.
Keywords in URLs are overrated for Google SEO. Create URLs for users. Also, you usually don’t even see them on mobile.
— johnmu of switzerland (personal) (@JohnMu) March 8, 2017
And in 2018, Mueller again minimized the importance of keywords in URLs for SEO:
I wouldn’t worry about keywords or words in the URL. In many cases, users don’t see the URLs anyway.
— johnmu of switzerland (personal) (@JohnMu) December 6, 2018
Best practice for URLs is to keep them short but descriptive.
This will help signal to a potential website visitor what it is about (if they can see the URL) and help them decide whether to click on the website.
When in doubt, you can’t lose by asking how it will affect a potential site visitor.
So if you have two main keywords relevant to the topic in your URL structure, that will be just fine.
If you go back to the “fishing fly” search result example, you’ll see that the number one result has no keyword in the URL.
However, in the number one position, Google still ranked it as the most relevant for that keyword phrase.
8. Best Way To Use Headings For SEO
Headings are like title tags because their role is to describe what the web page is about and what part of the web page is about.
John Mueller explained the best way to use the title:
“…what we use these titles for is we have this big piece of text or we have this big image and there’s a title above that, so maybe this title refers to this piece of text or this image.
So it’s not like there are five keywords in these titles, so this page will rank for these keywords, but more, here’s more information about that piece of text or that image on that page.”
A best practice for using titles is to describe what the page or part of the page is about.
Casey Markee had this to say about optimizing title elements:
“Headings on a page provide a road map for users and indexes to navigate through a piece of content.
Headlines have been horribly abused over the years to the point that Google has algorithmically targeted them for rewriting.
Focus on writing clear, concise titles that aren’t overloaded with keywords, use title-caps or sentence caps, and follow clear Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG).
Always use headings consecutively (never jump from H2 to H4 just because), don’t end each heading with a focus keyword, and never use CAPITAL MIDDLE in headings as some screen readers may confuse them with acronyms.”
9. Google Discover
Cindy Krum, Founder & The CEO of MobileMoxie – which offers mobile SEO tools – raves about Google Discover.
She shared these tips for Google Discover SEO:
“Google Discover is natively included on all Android phones and in the Chrome app for iOS. Because it has so many users, Discover can be a significant traffic driver. It’s a great way to reach enthusiastic and loyal site visitors.
Content is displayed to users who are interested in the topic, not because of keyword queries, which can make it difficult to report that it can be directly attributed to SEO efforts.
But Google needs to know what a website is about in order to show it to users who have expressed interest in certain topics. This means that on-page SEO is important.
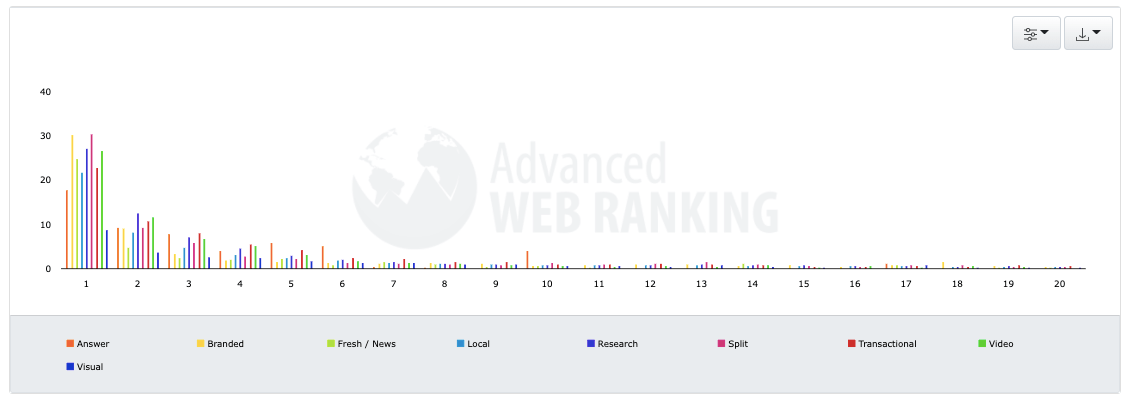
For greater visibility, it is important that pages have high-resolution images and pass all checks for Google’s mobile Page Experience assessment in Search Console.
It also helps if pages load quickly because the context in which Google Discover content is displayed is mobile.”
A common mistake people make with their featured image is using one that’s too small or not rectangular.
To ensure that Google displays your content in Google Discover, use an image that is at least 1200 pixels wide.
The rectangular image has the option to be displayed in its entirety. A square image will only be displayed as a smaller thumbnail, which will not stand out as much.
Speaking of highlighting, be sure to use featured images that are colorful.
Brightly colored images draw attention to themselves in Google Discover and can help drive clicks.
Also, use the maximum number of image review robots set in bulk:
10. AI For Content
Marketers tend to think of AI as a way to produce a lot of content faster.
(And often not so good content.)
The SEO best practice for AI is not about content generation, but about using AI to automate the entire content creation process.
Jeff Coyle, CEO of AI Content Automation Strategy at MarketMuse, explained SEO best practices for AI-powered content:
“Assess the entire lifecycle of content creation and management in your company to identify stages in the process that are manual and inefficient.
AI can improve every stage of content creation:
Finally, automation can be used in the promotion and optimization stages of the content lifecycle.
It is possible to improve each of these critical stages when perfecting the business content engine.
AI solutions for content can improve decision-making and research processes, making them faster and more successful.”
Jeff finished by sharing these best practices for getting the most out of automation:
“Make sure any speed improvement and automation has checks and balances for quality and performance so you can make improvements in volume, quality and content engagement/performance with AI, while growing trust in technology across your organization.”
11. SEO For Images
Images should ideally be colorful, but also light in weight, under 100 kb (and ideally under 50 kb).
I know that sounds unrealistic, but the truth is that image editing software like Photoshop can help create the smallest possible image that still looks great.
Images in the body of an article are great for breaking up the content and helping readers get to the end of the article.
But make sure the image is relevant to the content as it will help convey the theme or message of the content.
12. SEO For Product Pages
Cindy Krum is also an expert in optimizing product pages for SEO and conversions on mobile-sized websites.
She had a lot to share about best practices for optimizing product pages.
“Mobile product pages are a significant opportunity for SEO, but it can be different from what most SEOs are used to.
We’re seeing Google place more and more emphasis on Merchant Center Listings, so when you’re optimizing your product pages for SEO, it’s important to know if they’re ranking for your mobile shopping query.
If there is a free product listing module ranking for your keyword, it might be hard to beat that; it would be like beating the Knowledge Graph score.
We think users like Merchant Center pack into search results because they function as a quick price comparison, so it seems likely that Google will retain them.
In this case, especially for broad queries like this, the strategy for ranking product pages comes down to ranking in Free Merchant Center Listings – which is a whole new game!”
13. Best Practices For Category Pages
There is a long-standing idea in the search community that category pages are not useful, so they add noindex, follow robots to meta tag pages.
But that’s a big mistake – because then Google won’t index the category pages (as requested), and therefore Google won’t follow the links, because the page isn’t indexed.
So the best practice is to always allow search engines to index product pages.
Another best practice is to use unique snippets for each page.
Those excerpts are what will be displayed on the category pages. Using a snippet from the first few sentences of a web page for an excerpt is a missed opportunity.
Category pages are a great way to present a general page about a topic.
14. Best Practices For Review Websites
Google wants to rank product reviews that are real, not just product summaries; Learn about Google’s product review content guidelines.
When writing reviews, be sure to show product images and use as many as the customer needs.
If helpful, show product images used to illustrate the review section.
A key focus of Google’s guidelines is to encourage user-friendly product reviews.
The product review guidelines end with:
“When writing reviews, focus on the quality and originality of your reviews, not length… This will provide the most value to customers who read your reviews.”
A best practice for SEO on review websites is to provide product guidance and help customers make better decisions.
15. Structured Data For SEO
Joost De Valk, founder of the Yoast SEO Plugin, shared his advice for structured data best practices.
“When you’re optimizing your website, make sure you have all the important information not only in human-readable text, but also in structured, machine-readable data.
Whether it is the opening hours of your store, the (sale) price of a product in a web shop or the title and author of a news article on a news website: there is structured schema.org data for everything.
As Google’s structured data guidelines are constantly evolving, I would highly recommend using a plugin for such work, as it shifts the burden of updating that schema onto the plugin developer, instead of you.
Of course, this means you have to trust the plugin developer to actually do a good job for you, as well as understand the SEO impact.”
I agree with Joost that using a structured data management plugin is a best practice for SEO. Google’s structured data guidelines are constantly updated.
By using the plugin, you no longer have to spend time tracking changes in structured data guidelines and taking time to update structured data across your site.
16. Best Way To Do Internal Linking
Internal linking is a way to index content and help Google better understand what content is important.
Scott Hendison, CEO of Search Commander, Inc., offers some useful ideas about internal linking:
“I’m currently checking a huge website that someone migrated, where they (at least) included all 301 redirects, but didn’t fix the internal linking structure.
I simply use the Better Search Replacement plugin in WordPress to change tens of thousands of redirects and redirect chains to show the final destination of the URL. I guess I would call this tactic ‘returning your own internal link equity’.
It’s pretty basic, but I never fail to get a ranking boost when I do it on pages, which is quite often.
Redirects are always there, but no one bothers to fix the links within the content itself.
301 should of course be left in place, for old tags and external links, but finalizing the internal linking structure to have no redirects is something I’ve been a big believer in for a long, long time, and I’ve seen improvements since then – especially when there are redirect chains.
Some SEO tools will list redirects as a minor problem, but over time these types of problems add up, especially with chained redirects, and become bigger problems.
I strongly encourage clients to for repairs. They are easy to find and fix and can result in significant improvements.”
Joost had this to say about internal linking:
“When you’re optimizing a website, one of the first things to do is make sure you improve the internal links between pages.
Very often, websites will have very little or no internal links in their content, relying entirely on large navigation menus to get people moving.
In the interest of helping both your visitors and search engines, you should link related content to each other within that content.
This can often have dramatic effects on your rankings. There are tools and plugins that can help you easily find internal links, so you don’t have to know all the content on a site (I know I often don’t know about sites I’ve written tons of content for). ”
SEO consultant Chris Labbate offered more best practices for internal linking:
“When it comes to internal connectivity, I like to say that ‘Context is King.’
Here are what I believe are best practices for creating internal links, keeping semantic SEO in mind:
Try not to make connections at the beginning of a paragraph.
We all know that Google indexes internal links, but it also looks at the surrounding text around each link.
This is especially true if the anchor text is too generic, such as “click here” or “follow me”, Google is almost forced in this situation to look at the surrounding words to get additional relevance.
It also means you can use that approach for better internal connectivity.
Always pay special attention to the surrounding text of the internal anchor text.
Giving Google good context around your links can help give search engines some good information about the link, but also improve your rankings by explaining what the link can do for them and any other data related to user intent.”
17. Read Patents Carefully
An important SEO best practice is to research each best practice to determine if it is true.
What sometimes happens is that patents and research papers are misunderstood, and later these misunderstandings become false best practices.
Those kinds of bogus best practices are often based on a misinterpretation of what a Googler said, or what was published in a patent or research paper.
For example, a common SEO myth is that Google uses “brand mentions” as a sort of link-like ranking signal.
This myth originated in a patent related to the use of branded search queries as a type of citation signal, similar to a link.
The idea of the patent was that if users search with the website name plus keywords, then it can be considered a form of citation, although not a link, but implied as one.
The entire patent, from the opening paragraphs to the end of the patent, was explicitly focused on search queries containing a URL or website name plus a keyword phrase.
Somewhere in the middle of that patent was a paragraph that used the phrase “implied connection.”
This is a passage from the Google patent:
The system determines the number of independent connections for the group (step 302).
A link to a resource group is an incoming link to a resource in the group, ie. a connection that has a resource in the group as its target.
Links for a group can include express links, implied links, or both. Express connection, e.g. A hyperlink is a link included in a source resource that a user can follow to get to the target resource.
An implicit link is a reference to the target resource, e.g. a citation to the target resource, which is included in the source resource but is not an express link to the target resource.
Therefore, a resource in a group can be the target of an implicit link without the user being able to navigate to the resource by following the implicit link.
The SEO community took that sentence out of the context of the entire patent and then used that one sentence to create the idea that a link was implied when the URL was written, but no link.
This idea was further extended to mention the brand name.
This type of error is not uncommon.
Some SEO professionals still make the mistake of skimming the patent (without trying to understand it) and then stopping at a paragraph or two that seems to confirm the SEO idea they have.
That’s not how patents are read.
So, every time someone claims that a patent says Google is doing something, always look at the patent yourself.
The best practice for learning what Google can do (according to the patent) is to pay attention to the opening paragraphs.
In the opening paragraphs you will find the key to understanding what the patent is about. By doing this, you will be better able to avoid false best practices.
Understanding SEO
Understanding SEO can be baroque or minimal, depending on the individual.
The most common mistake is to focus on what Google might be doing.
If there’s a golden rule for SEO best practice, whether you’re doing keyword research or evaluating competitors, it’s this: Build your SEO strategy around how a site visitor or potential customer might react.
Featured image: HBRH/Shutterstock
Whether you invested early in SEO or are just starting out, it can still be a major driver of traffic and leads to your website. SEO is especially useful for locally focused businesses, those looking to reach more users with their content, and businesses hoping to adopt a multi-channel approach.
How can I improve my search engine ranking?
Improve your search engine rankings
- Understand your online customers.
- Use keywords on your website.
- Refresh your page content often.
- Get referrals from other websites.
- Use meta tags in your content.
- Stay up to date with the latest SEO techniques.
How does Google rank its search results?
To rank websites, Google uses web crawlers that scan and index pages. Each page is rated according to Google’s opinion of its authority and usefulness to the end user. Then, using an algorithm with over 210 known factors, Google orders them on the search results page.
How does Google choose the order of search results? Google works by crawling the web, ranking millions of existing pages and storing them in an index. When a user performs a search, Google can then scan its more organized index (rather than the entire web) to quickly find relevant results.
What is the elements of Google?
Google’s SERPs can display various elements: the search results themselves (so-called snippets), a knowledge graph, a featured snippet, an answer box, images, shopping results, and more. Depending on the type of query and the data that Google finds, some of these elements will be displayed.
What are the elements of Google? Google’s SERPs can display various elements: the search results themselves (so-called snippets), a knowledge graph, a featured snippet, an answer box, images, shopping results, and more.
What is a Google search result called?
Search engine results pages (SERPs) are the pages that search engines display in response to a user’s query. The main component of a SERP is the list of results returned by a search engine in response to a keyword query.
What is the box on the right of a Google search called?
Almost every search on Google displays an information box on the right side of the results page. This box, known as the Knowledge Graph, displays information such as the company’s name, phone number, a link to their website, hours of operation, as well as reviews and pictures.
What is the first search result called?
Title. Your headline is the first, and often the only, part of your search results that people read.
What is a search page called?
A search engine results page or SERP is the page you see after entering a query into Google, Yahoo or any other search engine.
Is Google a search engine?
Google Search is a fully automated search engine that uses software known as web crawlers that regularly scour the web to find pages to add to our index.
Why is Google a search engine?
Google’s success is believed to have come from its desire and ability to provide better results for every user. Understanding search intent and finding the most accurate and relevant web pages to match each query has allowed Google to set itself apart from the competition.
Is Google a search browser?
Examples of well-known search engines are: Google, Yahoo, Bing, DuckDuckgo, Baidu Internet Explorer. Some of the widely used web browsers are: Mozilla Firefox, Netscape Navigator and Google Chrome.
What is the difference between search engine and Google?
The browser contains its own database. Some of the popularly used web browsers are Google Chrome Mozilla Firefox and Netscape Navigator. Examples of prominent search engines are Google, Bing, Yahoo, Baidu Internet Explorer and DuckDuckgo. Multiple web browsers can be installed on a single system.
What are the main pillars of SEO?
Instead, SEO is supported by three distinct pillars: discoverability, relevance, and authority. Make sure your website keeps these three SEO concepts in mind for the future, and you’ll have a content marketing strategy that will increase your place on the search engine results pages (SERPs).
What are the 4 main components of SEO? Each component builds on and complements the others. The stronger the links between each of the 4 SEO components – technical SEO, on-page SEO, off-page SEO and content – the better the results. Being aware of connections will help us better understand how to make the best use of them.
What are the major pillars of SEO?
The four pillars of SEO include technical SEO, content, on-site optimization, and off-site SEO.
What are the 3 pillars of SEO Fiverr?
The three pillars of SEO: authority, relevance and experience.
What are the 3 parts of SEO?
EAT – short for expertise, authority and trust. A frequently used acronym that represents the three most important elements of SEO. Google wants to display websites that demonstrate expertise in their field, have authority based on various factors, and are trusted.
What are the 3 C’s of SEO?
Simply put, the basics of SEO can be boiled down to the 3 C’s: Content, Code and Credibility.



