Google’s new Useful Content update allows the search giant to help marketers create meaningful customer experiences that start with search.
Google announcing its search engine algorithm update has become less of a major news story over the years. Updates to popular searches are very frequent, so any news can be a blur that generates only a small amount of interest.
But this latest change from Google is bold, introduced with a user-friendly name and a significant user-friendly signal that marketers and consumers alike can embrace.
Google introduced Useful Content Update in its search engine. It evaluates how well the content satisfies the user. It provides Google with a tremendous opportunity to help marketers create a meaningful customer experience that begins with search.
How Helpful Content Update Works
Contents
- 1 How Helpful Content Update Works
- 2 Bringing Balance to SEO tactics
- 3 Putting Search Power in Hands of Creators
- 4 People Still Want Answers Through Search
- 5 How do you redesign or rewrite the content of your website to support SEO strategy?
- 6 Why is SEO important for content marketing?
- 7 Why should you update old content?
- 8 What are the 3 pillars of SEO Fiverr?

Useful Content Updates (HCU) is an algorithmic ranking signal. It examines how closely a given site page follows Google’s core search guidelines, such as providing meaningful descriptions, clear source attribution and original research and analysis in content. This is intended to lower the value of content that has been overly optimized for the effect of search engines.
At first blush, this signal does not feel new. Guidelines for finding dates again 2019; so many recommendations for HCU sounds like people have long shared to prevent black hat SEO tactics, a perspective familiar to SEO and marketing experts. Black hat SEO is a tactic that overly optimizes page elements to influence search engine query results.
But well-intentioned content tips to prevent deceptive tactics have jumped the shark, with content creators from various backgrounds playing various search engine optimization techniques that straddle close to Black SEO tactics. They make searchable content, but a lot of that content is not Wikipedia-style neutral tone. This type of content shows that other responses are good answers for readers, even if the keywords appear in metadata and H1 tags without any filler.
Moreover, some publishers are too fixated on the following algorithmic changes, even though the announced changes will be one of hundreds of algorithmic improvements. Panda, for example, is just one of roughly 500 search improvements according to Google.
Bringing Balance to SEO tactics
The HCU signal is part of a larger effort by Google to balance what we see in the content they find on their search engine. Google added suggestions this year that marketers can include pros and cons of products and services in their structured data. Adding this will appear in the query results rich snippets. Goggle offers a Rich Results Test to verify its recognition in its search engine.
In fact, the name Useful Content Update is a fun game of balancing expectations. It is a label in layman’s language. In the past year, Google’s search engine algorithm changes have been well-known by their code words, such as Pigeon, Hummingbird and Panda. But while the shift to choose a phrase that speaks to the general user seems minor on the surface, it represents the endgame of a series of algorithm changes that reflect the technical aspects of a query.
The idea behind Google’s most well-known algorithm change is to figure out how HTML elements on a web page are arranged relative to a query. Now the search algorithm can distinguish between the elements of the web page with sophistication. Moreover, SEO techniques have evolved in identifying where keywords can be better placed and regarding links as signals of interest.
Related Articles: How to Use Keyword Density in a Modern SEO Strategy
Putting Search Power in Hands of Creators
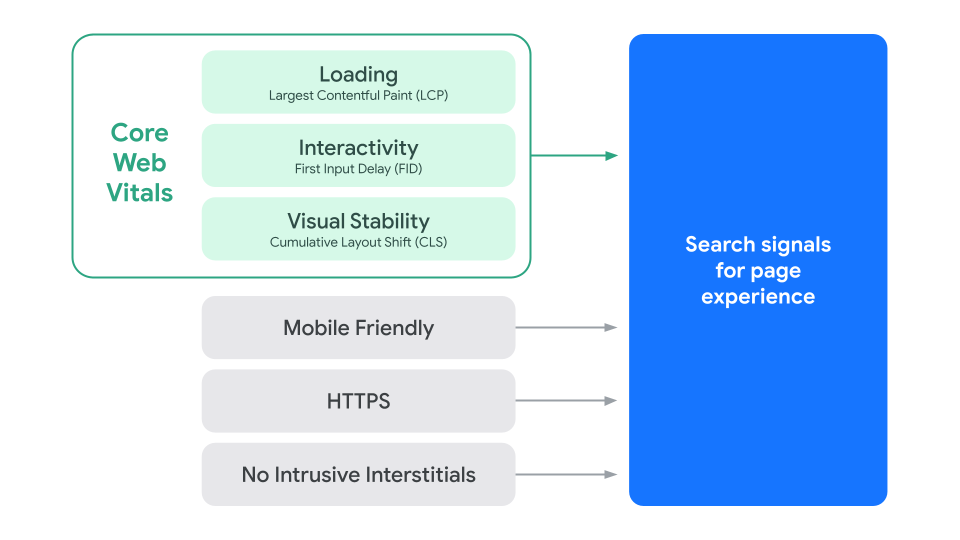
The Useful Content Update is the next step of the signal, directing the focus to the use of the creator rather than HTML. It encourages creators to choose their content in a more natural way for people to appreciate rather than the potential to focus more on page syntax. It also rebalances the publisher’s expectations in focusing on key changes, rather than a series of minor changes that may not have an impact on the customer experience or page content.
The change also acknowledges the different ecosystem that Google faces compared to the infancy of the search engine. Organic search is still the juggernaut when it comes to building capabilities for sales, and Google retains the lion’s share of search-generated traffic and usage.
But other platforms have emerged as the starting point of the customer journey, changing the customer experience as a result. People search on Amazon in the same vein as Google or Bing, usually with a product already in mind. Consumers at home will ask Alexa for services very close to how they would perform searches from a smartphone….and probably not on a laptop at home.
This means Google must account for these new attribution points while encouraging content providers to imagine these touch points when planning content. Such considerations appear in reporting adjustments to tools such as Google Analytics 4 and Google Search Console. Content is now part of the standard marketing strategy, and the material is measurable and helpful for attribution.
Related article: What Marketers Can Expect from Google Mum
People Still Want Answers Through Search

Moreover, not everyone who uses the search engine is only a customer or would-be customer. People turn to Google for a variety of purposes. People rely on Google search results for a variety of content that they perceive as factual and sound because they expect it to solve problems through advice, inspiration or guidance.
Thus, the Helpful Content Update illustrates how Google realizes the social cost of lingering bad content creation. Misinformation and its role in major cultural issues and political events in recent years have revealed how the product can be misused. Returning information accurately to the request is a start to overcome the problem.
You can be sure this will also trickle down in some capacity to YouTube. YouTube is the second largest search engine behind Google and is a hub for many online activities (see my post on CTV as an example). While YouTube videos have different optimization considerations than web pages, the philosophy behind Useful Page Updates will be adopted.
How do you redesign or rewrite the content of your website to support SEO strategy?

Website Redesign SEO Checklist
- Analyze your site now.
- Inventory your high performing content.
- Define your SEO goals.
- Optimize your existing content.
- Set up a 301 redirect.
- Update your site architecture.
- Optimize your page speed.
- Update your XML sitemap.
Why is SEO important for content marketing?
The goal of SEO is to get the right eyes on the right piece of content, every time. Through targeted optimization, technical tune-up, and regular adjustments for this, an SEO expert helps drive traffic through more organic sources, like search engines.
What is SEO & amp; Why is it important? SEO stands for search engine optimization—the practice of increasing the quantity and quality of traffic to your website through organic search engine results. The ultimate goal of SEO for business is to generate organic trafficâsearchers clicking through to your website from the search engine results page (SERP).
How important is SEO for content marketing?
Without SEO and content strategy, your content will never be found online. Many marketers see SEO and content marketing as two different strategies but they are connected and complement each other well. Without creating high quality content, you will never be able to profit from it.
Why SEO is important for content strategy?
Having an SEO strategy is important because it helps you stay on track when creating content. Instead of just creating what you want people to think about, your strategy will ensure that you create content that people are looking for.
Does SEO help with content marketing?
Benefits for your SEO In addition to creating trust and building relationships with your audience, content marketing helps you with search engine optimization (SEO). An important part of SEO is writing quality content, focused on your users.
Does content marketing include SEO?
In addition to building trust and building relationships with your audience, content marketing helps you with your search engine optimization (SEO). An important part of SEO is writing quality content, focused on your users.
Is SEO part of content marketing?
SEO refers to the technical process of improving the quality of traffic and attracting maximum visitors to your website. On the other hand, content marketing focuses on using valuable and relevant content to drive profitable customer or client actions. SEO without content marketing is like a body without a soul.
What is included in content marketing?
Content marketing is the development and distribution of relevant, useful content—blogs, newsletters, white papers, social media posts, emails, videos, and more—to current and potential customers.
Why should you update old content?
By updating old content, you can get Google to crawl your site more often without needing to publish more often. The more Google crawls your site, the more likely your latest information will appear in search results after publication, which gives you an advantage in your search engine results rankings.
What are the 3 pillars of SEO Fiverr?
The Three Pillars of SEO: Authority, Relevance, and Experience.
What are the 3 pillars of SEO? Instead, SEO is supported by three different pillars: discovery, relevance, and authority. Make sure that your website keeps these three front-end SEO concepts in mind, and you will have a content marketing strategy that will improve your place in search engine results pages (SERPs).
What are the major pillars of SEO?
The four pillars of SEO include technical SEO, content, on-site optimization, and off-site SEO.



