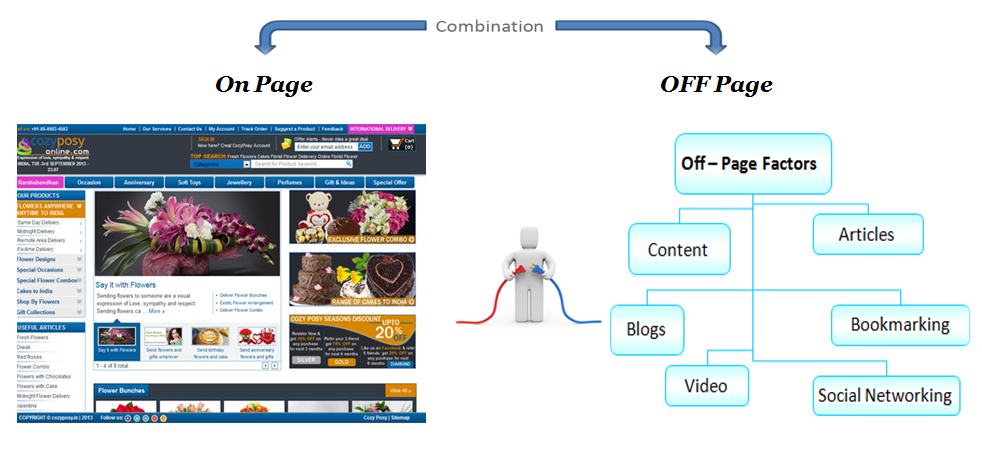
Off-page SEO is one of the most difficult parts of digital marketing.
It can seem like there are more ways to get it wrong than to get it right.
Somewhere in between the “do this, not that” recommendations are useful approaches to promoting websites that don’t cause you to look over your shoulder.
Off-page SEO traditionally means getting links.
And since links continue to be an important ranking factor, off-page SEO is an important part of SEO.
Google’s John Mueller acknowledged the importance of links when he said:
“Links are very important for us in the beginning to find content.
So if no one ever links to your website, it’s hard for us to recognize that it even exists.
But Mueller has also said the links should not be made:
In general, you should not link to your site. I recommend that you consult our webmaster guidelines for more information.
— 🥔 johnmu (personal) updated for 2022 🥔 (@JohnMu) November 10, 2021
Google’s documentation on how to do SEO focuses primarily on on-page optimization (also known as on-page SEO).
Google SEO advice rarely covers off-page SEO except in the context of what not to do.
By approaching it realistically and with the clear eye of a pragmatist, it is possible to navigate an off-page SEO strategy that stays within the narrow boundaries defined by Google – and make more money.
What Is Off-Page SEO?
Contents
- 1 What Is Off-Page SEO?
- 2 On-Page SEO Versus Off-Page SEO
- 3 Why Off-Page SEO Is Important
- 4 Three Kinds Of Links
- 5 Guest Posting For Links… Not
- 6 Guest Post For Higher Earnings, Not Links
- 7 Off-Page SEO Is Site Promotion
- 8 What are the types of off page SEO?
- 9 What is main step for off-page SEO?
- 10 What are the two techniques of SEO?
- 11 What is off page SEO checklist?
The narrow definition of off-page SEO is: it’s link building.
The broad definition includes off-site promotional activities, including press releases and links (with or without nofollow) and brand awareness campaigns, which may include publication on other sites and newsletters.
SEO is usually discussed in direct relation to attributed search rankings.
If something is done for the purpose of SEO, better rankings and more search traffic can be expected.
And that’s because in the early days of SEO, search analytics showed which keywords were responsible for each visitor to a search-based site.
So it was easy to attribute search rankings directly to traffic.
And it was possible to attribute clicks from search results directly to conversions based on search traffic.
This made it easy to connect the dots between SEO activities, rankings and revenue.
But this is no longer possible – because browsers hide keywords.
And it made it easier to start thinking about SEO in terms of traffic and revenue, even though it can only be indirectly attributed to SEO.
Anyone who has ever worked in the B2B niche knows that there is much more to growing online traffic than what is available through search engines.
Search traffic is relatively low for many B2B keyword phrases.
For B2B marketers, survival often depends on reaching potential customers who may not even be aware the solution exists—as is the case with specialized tools such as organizational chart software or performance management applications.
Although advertising activity does not directly affect search traffic, it does affect traffic in the short term. As it turns out, this can affect search traffic in the long run.
No one can search for a product or company if they don’t know either exists.
Underscoring the importance of advertising, Google filed a patent that describes how branded searches can be used in a similar way to links to associate a business with a search term and place that business higher in search results.
From this perspective, it makes sense to include online advertising activities in the off-page SEO description.
On-Page SEO Versus Off-Page SEO

On-page SEO is optimizations made on a website that make it easier for search engines to crawl and understand.
This includes internal linking, using proper canonicalization, editing content for clarity, creating descriptive title tags, and writing unique meta descriptions.
On-page SEO ranking factors depend on what the page is relevant to and are considered a stronger signal than off-page SEO factors.
Therefore, content is considered the strongest ranking signal.
But without off-page SEO, a website will struggle to rank, especially in highly competitive markets.
Off-page SEO helps search engines discover web pages to crawl them and understand what those pages are about. It’s best to think of off-page SEO as an advertising activity that involves attracting links. But it can also include promotional activities to let consumers know the company exists and what it does.
The documentation available on Google for on-page SEO is extensive. This is not the case with off-page SEO, presumably because providing this information can lead to ranking changes.
Why Off-Page SEO Is Important

Off-page SEO is important because a website that lacks citations from other sites is like a site that is not worth crawling and indexing.
Since off-page ranking factors like links measure a site’s importance, missing links can very well contribute to stagnant search traffic.
It’s no different than a car without gas.
The most accurate description of what makes off-page SEO important is that it gives a site a boost by helping it rank higher for more keyword phrases.
While SEO professionals like to think of abstract concepts like website authority when it comes to links, Google doesn’t actually have any metric for authority.
Google often says it tries to rank authoritative content. But the word is generally used in the context of the quality of the content itself – not as a stand-alone ranking factor that flows into a web page and gives it authority.
Google Webmaster Trends analyst John Mueller debunked the idea that Google uses an authority meter.
“Generally, Google doesn’t value site authority.
So we don’t give you an authority score and say it’s an overall authority score for your website. It’s not something we would implement here.”
Another misconception about links is that they help build domain authority.
The concept of domain authority has its roots in the early days of SEO, when Google still displayed the PageRank values of web pages.
It was clearly seen that sites with high PageRank scores were ranked better than sites with lower PageRank scores.
The home pages of these sites had the highest PageRank scores.
So it was understood (at the time) that domains with a high PageRank score were better.
Since domains with high PageRank scores were considered authoritative, it was easy to tell that they were authoritative domains.
Anyone could see PageRank scores and how domains with high PageRank ranked higher than domains with lower PageRank.
This led to the belief in the concept of “domain authority”.
But Google never used any domain authority metrics.
The concept of domain authority was just a loose idea based on visually verifiable things.
Finally, Google adjusted the ranking of web pages so that PageRank scores played less of a role in deciding which pages ranked highest.
Relevancy then began to play a larger role in determining page ranking.
It took more than PageRank to get a page ranked, and the proof was again in the search results.
It could be seen that web pages with low PageRank scores were ranked higher than web pages of sites with higher PageRank scores.
But the idea of domain authority persisted.
Articles claiming that Google uses domain authority never cite any patent, research, or statement by a Google employee to support their claims (since there is no official confirmation).
In a Reddit AMA, Google’s John Mueller responded to the question of whether domain authority exists with a witty response:
“Of course there is, it’s a Moz tool.”
Three Kinds Of Links

In the SEO Starter Guide, Google docs clearly approve of promoting your website by telling others about it.
Here’s what Google has to say about link acquisition:
“While most links to your site are added incrementally as people discover and link to your content through search or other means, Google understands that you want to let others know about the hard work you’ve put into your content.
Effective promotion of new content helps to discover those who are interested in the same topic faster.
Although Google follows this statement with a warning that promoting a site at “extreme” levels can damage a site’s reputation, the advice still leaves plenty of room for website promotion.
Here are three types of links that can be found safely:
1. Research, Write, Tell Others About It
During the content planning stage of a website, it is important to research which sites are linking to the content pages of that particular topic.
One way to do this is to identify which sites are being linked to, and most importantly, why those pages are being linked out.
Every link strategy I create for a client always starts with researching which sites are linking and identifying the topics that trigger them to link.
Content writing happens after identifying the right content to publish.
The biggest mistake businesses make is writing content and then getting links to it. It doesn’t always work, no matter how good the content is.
Some sites consistently link to smart content on trending topics, such as very popular media.
Other sites tend to link out according to the era.
Every site that links has a reason for linking. Find that pattern and write for it.
2. Be Proactive About Getting Quoted
There’s a service called Help A Reporter Out (HARO) where publishers ask qualified individuals to provide quotes on topics – and perhaps a link to a website.
Arguably, HARO has been overpowered for the last 10 years due to the heavy competition from link producers swarming the system for links.
And some publishers hang a quote but never submit it.
For example, it has been my experience that some publishers abuse the system to collect quotes and article ideas from others without ever intending to cite, much less link, any of the contributors.
Thus, a whole business model has emerged that helps companies acquire so-called HARO links.
But why crunch like a pigeon pecking for crumbs? There is a better way.
And so you have to be proactive and approach quality sites that you want a link from.
Everyone loves a gift – and there’s no better gift for a content publisher than an article that writes itself.
The best way to do this is to research or compile relevant readership statistics for any publications that are perfect for a link.
As long as the topic is very current, quoting in a prepared article created by a press contact is a good way to get links.
Be sure to request that the article be embargoed, which means that it will not be published until a certain date.
For added impact, publish the entire data set on your website, then forward some of that data to publishers and ask them to consider linking to a page with the full report.
In the old days, people created infographics, creating a visual representation of government statistics by turning dry text into an easier-to-visualize infographic.
But people consume media on mobile phones, and infographics don’t always look good on mobile devices.
The infographic approach to off-page SEO can be considered an outdated practice.
In the long run, it may make more sense to compile a list of recommended sites for publication. Then research each site to see what relevant article topics are being published, what sources they link to, and how articles are featured that may be open to entertainment.
They also don’t have to be sites that offer linking opportunities.
Positioning your business name in front of tens of thousands of potential customers is hugely valuable.
3. Good Old Resource Links
Some sites still publish links to sites that provide certain types of resources such as downloads, templates, how-to’s, patterns, etc.
Websites love to link to useful content.
But again, don’t create content and find someone to link to it.
Find out who is linking to the resources and then create content like that.
Be sure to give it a great angle, a twist that sets it apart from other sites.
Guest Posting For Links… Not
Guest posting has been officially off the table since 2014, when Matt Cutts (then a Google engineer) made a public post that guest posting for links was over.
“So stick the fork in: guest blogging is done; it’s just gone too spammy. In general, I don’t recommend accepting a guest blog post unless you are willing to vouch for someone personally or know them well.
I also do not recommend relying on guest posts, guest blog sites, or guest blog SEO as a link building strategy.
Back in 2020, Google’s John Mueller explained that Google’s machine learning algorithms had a lot of training data to help identify links in guest posts and automatically devalue them so they don’t help sites rank better.
Here’s what he had to say about links guest posts:
“The other thing is, because it’s so old, we have a lot of training data for our algorithms. I wouldn’t be surprised if most of these links are just automatically ignored.
He then suggested doing something useful instead:
“If this work is for ignored links, why not do something useful instead?”
Guest Post For Higher Earnings, Not Links
A better approach to guest posts is to use them to raise awareness of your site in front of an audience that might be interested.
SEO professionals provide an opportunity to increase sales by claiming links.
Why not just guest post to increase sales? Isn’t money the whole point of link building and search marketing to begin with?
There are many ways to put your product in a favorable light, forget about links and just do it for the sake of sales.
Making money is what marketing is all about, so make money while everyone else is racking their brains trying to figure out how to link to a site.
This is true off-page SEO because as people become familiar with the site, it spreads through word of mouth – and then Google realizes that the site is popular, meaning a site that people expect.
There is even a Google patent on how Google can use branded search queries in the form of links.
I wrote about a Google patent using search queries that include brand names as if they were links here: Does Brand Mention Matter to Google’s Algorithm?
This shows that raising awareness can indirectly affect rankings.
The importance of this is to emphasize that off-page SEO does not necessarily have to involve links.
Off-Page SEO Is Site Promotion
It can be helpful to think of off-page SEO as something that encompasses more than just the limited scope of link building.
For this, you have to think about strategies to bring the company in front of thousands of decision makers.
Link builders leave behind many valuable and useful opportunities to increase sales and indirectly generate popularity signals that search engines can use.
Off-page SEO is useful for promoting a website to increase rankings, traffic and revenue.
Featured Image: Myvisuals/Shutterstock
What are the types of off page SEO?
Off-page SEO activities
- Brand Mentions.
- By commenting.
- Forums.
- Developing an influencer.
- Guest author.
- Broken link building.
- A social network.
- Social bookmarking.
What is Off Page SEO? On-page SEO refers to SEO factors and techniques that focus on optimizing the aspects of your website that are under your control. Off-page SEO refers to SEO factors and strategies that focus on promoting your site or brand across the web.
How many types of off-page SEO are there?
| S no | Off-page SEO techniques | The process |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Creating shareable content | Hard |
| 2 | Developing an influencer | Moderate |
| 3 | Contribute as a guest author | Moderate |
| 4 | Broken link building | Moderate |
What is off-page SEO?
“Off-page SEO” (also called “off-site SEO”) refers to actions taken outside of your website to influence your ranking on search engine results pages (SERPs). In addition to on-page SEO, they also include several basic SEO factors that help a site rank.
Which of the following is an example of off-page SEO?
Brand mentions are a good off-page SEO example to try because they are much more reliable. Without a brand or website link, the target owner has nothing to gain. Therefore, the host site will more than likely give the brand an honest recommendation.
Which things are included in off-page SEO?
Off-page SEO includes activities outside of the website that aim to improve the site’s ranking in search engines. Common off-page SEO activities include building backlinks, encouraging branded searches, and increasing engagement and sharing on social media.
Which is example of on-page SEO?
Some examples of on-page SEO activities include: Optimizing title tags and meta descriptions. Writing comprehensive and high-quality content. Cleaning up the site’s code.
What is main step for off-page SEO?
Off-page SEO includes activities outside of the website that aim to improve the site’s ranking in search engines. Common off-page SEO activities include building backlinks, encouraging branded searches, and increasing engagement and sharing on social media.
What is the most important part of off-site SEO? Off-Page SEO Tactic #1: Link Building. Given Google’s algorithm, link building remains an integral part of any off-page SEO strategy. But it’s important to understand how best to build links for your website and niche. Earning backlinks from high authority websites will help position your site as an authority.
What is off-page SEO and what is the best?
Off-page SEO refers to all the things you can do outside of your website to help you improve your SERP position: link building, forums, influencer outreach, and content marketing, to name a few. In layman’s terms, off-page SEO helps search engines understand what others think of your product, services or website.
What is off page SEO with examples?
While earning links from external websites is the most commonly used off-page SEO strategy, almost any activity that a) takes place outside of your website and b) helps improve your search engine ranking can be considered “off-page SEO”. ” These include, for example, social media marketing. Guest blogging.
What is a good off page SEO score?
If you’re interested in a “good” off-page SEO score, look at the following breakdown: 70 or above: Excellent – You have some areas where you can improve your website. 41-69: Good – You have some areas where you can improve your website.
What is off page SEO in simple words?
Off-page SEO includes activities on or behind the scenes of your website. Technical SEO refers to activities that directly affect the indexing and indexing of your site by search engines. For example, site speed optimization, structured data and more.
What are the two techniques of SEO?
SEO techniques fall into two broad categories: White Hat SEO – techniques that search engines recommend as part of good design. Black Hat SEO – techniques that are not approved by search engines and whose impact is tried to be minimized.
What is off page SEO checklist?
Get links from relevant and authoritative websites on the topic. Linking site popularity, relatability to topic, anchor text, credibility and authority. Creating positive reviews sends a strong signal to search engines about the credibility and authority of your niche topic.
What is Off-Site SEO? “Off-page SEO” (also called “off-site SEO”) refers to actions taken outside of your website to influence your ranking on search engine results pages (SERPs). In addition to on-page SEO, they also include several basic SEO factors that help a site rank.
What is SEO checklist?
On-Page SEO Checklist. On-page SEO is the process of optimizing the actual content of your page. This includes optimizations for visible content and source code content.
What is SEO and how it works?
Well, SEO stands for “Search Engine Optimization,” which is getting traffic from free, organic, editorial, or organic search results on search engines. Its purpose is to improve your website’s position on search results pages. Remember, the higher a website is, the more people will see it.
What is technical SEO checklist?
Technical SEO is an integral part of any SEO strategy, so the site must meet all search engine recommendations. The technical audit checklist includes several aspects to analyze and rank the technical parameters of the content and structure of the website.